Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format / Paraphrasing in APA

Paraphrasing in APA
Paraphrasing is the art of putting information into your own words while writing a research paper, in order to maintain the academic integrity of your project. This is important because you need to use solid evidence as a researcher, but you need to put information into the proper format to avoid plagiarism. The American Psychological Association (APA) created a writing style in 1929 that calls for uniformity and consistency in giving credit to sources in your research.
How to properly paraphrase
If you do not properly paraphrase your source material following the APA style, you are at the risk of losing credibility as a writer and possibly plagiarizing. Although paraphrasing is not difficult, it does take time and a little forethought to do it correctly. There are several steps you should follow in order to achieve success.
1. Read the original source
The first step in creating an effective paraphrase is to carefully read the original source. Read it the first time to get the overall understanding, and then do a second closer reading in order to gather details and material that will help you formulate your argument.
2. Take notes in your own words
After reading the original source and determining what details can help you formulate your argument, take a minute to jot down some notes. Be careful to put everything into your own words. Change the structure of the sentence as well as the vocabulary.
Also, take a moment to take notes on the context of the source. Why was it written? Who wrote it? When was it written?
3. Construct a paraphrase
In order to construct a paraphrase, you need to include the same information, but with different sentence structure and different vocabulary. APA rules say that a paraphrase should be approximately the same length as the original.
You also need to add contextual text around the paraphrase so it fits within your paper.
4. Double check the original source to avoid duplication
Although an extra step, it is always a good idea to read through the original source one more time to make sure that you have chosen different words and varied the sentence structure. This is a good time to add the APA requirements of author and year of the source so that you have it handy.
5. Include an APA in-text citation
Even though you are putting a paraphrase into your own words, APA requires an in-text citation for paraphrasing. You can create a parenthetical citation or a narrative citation to accomplish this.
Remember: All in-text citations will also need a corresponding APA reference in the APA reference page . For this article, we’re just focusing on in-text citations in paraphrases.
For both types of in-text citation, you will need the following source information:
- Author’s last name
- Year published
- single page: p. #
- page range: pp. #-#
Parenthetical citation
For an APA parenthetical citation , write your paraphrase and then add the author and year in parenthesis at the end. Use a comma between the author and the year inside the parenthesis, and put the period for the end of the sentence outside the parenthesis.
Oh, say can you see by the dawn’s early light What so proudly we hailed at the twilight’s last gleaming? (Key, 1814).
My parents traveled from Italy to Germany and then France. As the oldest child, I traveled with them after being born in Naples. They were very close, and shared that love they had for each other with me (Shelley, 1818, p. 78).
Narrative citation
In a narrative citation, you introduce the author’s name as part of the sentence, and put the year in parenthesis.
Francis Scott Key (1814) wrote very special words while overlooking a battle: Oh, say can you see by the dawn’s early light, what so proudly we hailed at the twilight’s last gleaming?
For further details, visit this guide on APA in-text citations.
Paraphrasing example
Franklin Delano Roosevelt gave an inaugural address in January 1933 during the Great Depression. This is an excerpt taken from an online source :
This is preeminently the time to speak the truth, the whole truth, frankly and boldly. Nor need we shrink from honestly facing conditions in our country today. This great Nation will endure as it has endured, will revive and will prosper….
1. Read original source text
In order to paraphrase, read through the text once to get the gist of it, and then again for deeper understanding. The context of this passage is also significant. It was given by a U.S. president during the Great Depression. What do you think he was trying to achieve?
Next take notes in your own words. Without immediately looking at the text, jot down what you think is the main point or concept of it. Next, take notes on the context of the source (you can look at the source for this).
For this passage, a few example notes could be:
- Facing truth
- Harsh current reality
- Believing that this great nation will endure and eventually prosper again
- Speech by President Roosevelt in 1933
- Given during the Great Depression
- He was addressing his citizens
Now’s the time to construct the paraphrase. Based on the notes above, a paraphrase would look something like this:
With his inaugural speech, Roosevelt was carefully trying to prepare citizens of the Nation to face the harsh reality that the Great Depression had caused, while also reassuring them that the country would endure and eventually prosper again.
4. Double check with the original source
The paraphrase above doesn’t not look too similar to the original, but we could still change a few words that were also in the original phrase (like “Nation,” “endure,” and “prosper). Revised, it looks like this:
With his inaugural speech, Roosevelt was carefully trying to prepare citizens of the United States to face the harsh reality that the Great Depression had caused, while also reassuring them that the country would eventually bounce back .
5. Add an APA in-text citation
An APA in-text citation means including the source’s author, year published, and page numbers (if available). The paraphrase already has the author’s name, but the year published needs to be added in parentheses. This is from an online source so no page number is needed.
With his inaugural speech, Roosevelt (1933) was carefully trying to prepare citizens of the United States to face the harsh reality that the Great Depression had caused, while also reassuring them that the country would eventually bounce back.
Examples of poor paraphrasing
Most people who fail at paraphrasing use the same sentence as the original source, and just change a word or two. If this is the case, the paraphrase would look something like this:
This great country will endure as it has endured, will come back to life and will prosper. So, first of all, let me show my strong belief that the only thing we have to worry about is fear itself…”
Another problem with paraphrasing occurs when you do half the job. Although the first and third sentences change the sentence structure and vocabulary in the sample below, there are some sections that are taken word-for-word from the original.
“From Italy they visited Germany and France. I, their eldest child, was born at Naples, and as an infant accompanied them in their rambles. I remained for several years their only child. Much as they were attached to each other, they seemed to draw inexhaustible stores of affection from a very mine of love to bestow them upon me.
Paraphrase:
My parents visited Italy and then Germany and France. I, their eldest child, was born at Naples. I traveled with them and was their only child for a few years. They loved each other and they seemed to draw inexhaustible stores of affection from a very mine of love.
In addition to the word-for-word similarities, this paraphrase doesn’t mention the original source’s author, year published, or page number (Shelley, 1818, p. 78).
Key takeaways
- In order to avoid plagiarism, APA delineates the way to give credit to sources when you are paraphrasing.
- In APA style, parenthetical citations demand the author and year of source.
- In order to create a stellar paraphrase, you need to change the structure and the words, but keep the main idea intact.
Published October 28, 2020.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
APA Citation Examples
APA Formatting
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on April 8, 2022 by Courtney Gahan and Jack Caulfield. Revised on June 1, 2023.
Paraphrasing means putting someone else’s ideas into your own words. Paraphrasing a source involves changing the wording while preserving the original meaning.
Paraphrasing is an alternative to quoting (copying someone’s exact words and putting them in quotation marks ). In academic writing, it’s usually better to integrate sources by paraphrasing instead of quoting. It shows that you have understood the source, reads more smoothly, and keeps your own voice front and center.
Every time you paraphrase, it’s important to cite the source . Also take care not to use wording that is too similar to the original. Otherwise, you could be at risk of committing plagiarism .
What is your plagiarism score?
Compare your paper with 99.3 billion webpages and 8 million publications.
- Best plagiarism checker of 2021
- Plagiarism report & percentage
- Largest plagiarism database
Scribbr Plagiarism Checker
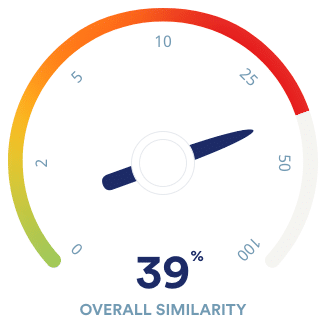
Table of contents
How to paraphrase in five easy steps, how to paraphrase correctly, examples of paraphrasing, how to cite a paraphrase, paraphrasing vs. quoting, paraphrasing vs. summarizing, avoiding plagiarism when you paraphrase, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about paraphrasing.
If you’re struggling to get to grips with the process of paraphrasing, check out our easy step-by-step guide in the video below.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Putting an idea into your own words can be easier said than done. Let’s say you want to paraphrase the text below, about population decline in a particular species of sea snails.
Incorrect paraphrasing
You might make a first attempt to paraphrase it by swapping out a few words for synonyms .
Like other sea creatures inhabiting the vicinity of highly populated coasts, horse conchs have lost substantial territory to advancement and contamination , including preferred breeding grounds along mud flats and seagrass beds. Their Gulf home is also heating up due to global warming , which scientists think further puts pressure on the creatures , predicated upon the harmful effects extra warmth has on other large mollusks (Barnett, 2022).
This attempt at paraphrasing doesn’t change the sentence structure or order of information, only some of the word choices. And the synonyms chosen are poor:
- “Advancement and contamination” doesn’t really convey the same meaning as “development and pollution.”
- Sometimes the changes make the tone less academic: “home” for “habitat” and “sea creatures” for “marine animals.”
- Adding phrases like “inhabiting the vicinity of” and “puts pressure on” makes the text needlessly long-winded.
- Global warming is related to climate change, but they don’t mean exactly the same thing.
Because of this, the text reads awkwardly, is longer than it needs to be, and remains too close to the original phrasing. This means you risk being accused of plagiarism .
Correct paraphrasing
Let’s look at a more effective way of paraphrasing the same text.
Here, we’ve:
- Only included the information that’s relevant to our argument (note that the paraphrase is shorter than the original)
- Introduced the information with the signal phrase “Scientists believe that …”
- Retained key terms like “development and pollution,” since changing them could alter the meaning
- Structured sentences in our own way instead of copying the structure of the original
- Started from a different point, presenting information in a different order
Because of this, we’re able to clearly convey the relevant information from the source without sticking too close to the original phrasing.
Explore the tabs below to see examples of paraphrasing in action.
- Journal article
- Newspaper article
- Magazine article
| Source text | Paraphrase |
|---|---|
| “The current research extends the previous work by revealing that to moral dilemmas could elicit a FLE [foreign-language effect] in highly proficient bilinguals. … Here, it has been demonstrated that hearing a foreign language can even influence moral decision making, and namely promote more utilitarian-type decisions” ( , p. 874). | The research of Brouwer (2019, p. 874) suggests that the foreign-language effect can occur even among highly proficient bilinguals, influencing their moral decision making, when auditory (rather than written) prompting is given. |
| Source text | Paraphrase |
|---|---|
| “The Environmental Protection Agency on Tuesday proposed to ban chrysotile asbestos, the most common form of the toxic mineral still used in the United States. … Chlorine manufacturers and companies that make vehicle braking systems and sheet gaskets still import chrysotile asbestos and use it to manufacture new products. “The proposed rule would ban all manufacturing, processing, importation and commercial distribution of six categories of products containing chrysotile asbestos, which agency officials said would cover all of its current uses in the United States” ( ). | Chrysotile asbestos, which is used to manufacture chlorine, sheet gaskets, and braking systems, may soon be banned by the Environmental Protection Agency. The proposed ban would prevent it from being imported into, manufactured in, or processed in the United States (Phillips, 2022). |
| Source text | Paraphrase |
|---|---|
| “The concept of secrecy might evoke an image of two people in conversation, with one person actively concealing from the other. Yet, such concealment is actually uncommon. It is far more common to ruminate on our secrets. It is our tendency to mind-wander to our secrets that seems most harmful to well-being. Simply thinking about a secret can make us feel inauthentic. Having a secret return to mind, time and time again, can be tiring. When we think of a secret, it can make us feel isolated and alone” ( ). | Research suggests that, while keeping secrets from others is indeed stressful, this may have little to do with the act of hiding information itself. Rather, the act of ruminating on one’s secrets is what leads to feelings of fatigue, inauthenticity, and isolation (Slepian, 2019). |
Once you have your perfectly paraphrased text, you need to ensure you credit the original author. You’ll always paraphrase sources in the same way, but you’ll have to use a different type of in-text citation depending on what citation style you follow.
| (Brouwer, 2019, p. 874) | |
| (Brouwer 874) | |
| 1. Susanne Brouwer, “The Auditory Foreign-Language Effect of Moral Decision Making in Highly Proficient Bilinguals,” 40, no. 10 (2019): 874. https://doi.org/10.1080/01434632.2019.1585863. |
Generate accurate citations with Scribbr
Don't submit your assignments before you do this.
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
It’s a good idea to paraphrase instead of quoting in most cases because:
- Paraphrasing shows that you fully understand the meaning of a text
- Your own voice remains dominant throughout your paper
- Quotes reduce the readability of your text
But that doesn’t mean you should never quote. Quotes are appropriate when:
- Giving a precise definition
- Saying something about the author’s language or style (e.g., in a literary analysis paper)
- Providing evidence in support of an argument
- Critiquing or analyzing a specific claim
A paraphrase puts a specific passage into your own words. It’s typically a similar length to the original text, or slightly shorter.
When you boil a longer piece of writing down to the key points, so that the result is a lot shorter than the original, this is called summarizing .
Paraphrasing and quoting are important tools for presenting specific information from sources. But if the information you want to include is more general (e.g., the overarching argument of a whole article), summarizing is more appropriate.
When paraphrasing, you have to be careful to avoid accidental plagiarism .
This can happen if the paraphrase is too similar to the original quote, with phrases or whole sentences that are identical (and should therefore be in quotation marks). It can also happen if you fail to properly cite the source.
Paraphrasing tools are widely used by students, and can be especially useful for non-native speakers who may find academic writing particularly challenging. While these can be helpful for a bit of extra inspiration, use these tools sparingly, keeping academic integrity in mind.
To make sure you’ve properly paraphrased and cited all your sources, you could elect to run a plagiarism check before submitting your paper. And of course, always be sure to read your source material yourself and take the first stab at paraphrasing on your own.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Critical thinking
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
To paraphrase effectively, don’t just take the original sentence and swap out some of the words for synonyms. Instead, try:
- Reformulating the sentence (e.g., change active to passive , or start from a different point)
- Combining information from multiple sentences into one
- Leaving out information from the original that isn’t relevant to your point
- Using synonyms where they don’t distort the meaning
The main point is to ensure you don’t just copy the structure of the original text, but instead reformulate the idea in your own words.
Paraphrasing without crediting the original author is a form of plagiarism , because you’re presenting someone else’s ideas as if they were your own.
However, paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you correctly cite the source . This means including an in-text citation and a full reference, formatted according to your required citation style .
As well as citing, make sure that any paraphrased text is completely rewritten in your own words.
Plagiarism means using someone else’s words or ideas and passing them off as your own. Paraphrasing means putting someone else’s ideas in your own words.
So when does paraphrasing count as plagiarism?
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if you don’t properly credit the original author.
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if your text is too close to the original wording (even if you cite the source). If you directly copy a sentence or phrase, you should quote it instead.
- Paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you put the author’s ideas completely in your own words and properly cite the source .
Try our services
To present information from other sources in academic writing , it’s best to paraphrase in most cases. This shows that you’ve understood the ideas you’re discussing and incorporates them into your text smoothly.
It’s appropriate to quote when:
- Changing the phrasing would distort the meaning of the original text
- You want to discuss the author’s language choices (e.g., in literary analysis )
- You’re presenting a precise definition
- You’re looking in depth at a specific claim
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Gahan, C. & Caulfield, J. (2023, June 01). How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/how-to-paraphrase/
Is this article helpful?
Courtney Gahan
Other students also liked, how to write a summary | guide & examples, how to quote | citing quotes in apa, mla & chicago, how to avoid plagiarism | tips on citing sources, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

APA Citation Guide (7th edition) CGS
- Advertisments
- Books & e-Books
- Book Reviews
- Class Notes, Class Lectures and Presentations
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Generative AI
- Government Documents
- Images, Charts, Graphs, Maps & Tables
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Personal Communication (Interviews, Emails)
- Social Media
- Videos & DVDs
- When Creating Digital Assignments
- When Information Is Missing
- Works Cited in Another Source
Paraphrasing
- Reference List & Sample Writing
- Annotated Bibliography
When you write information from a source in your own words, cite the source by adding an in-text citation at the end of the paraphrased portion as follows:
Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt, 1993).
Note : If you refer to the author's name in a sentence you do not have to include the name again as part of your in-text citation, instead include the year of publication following his/her name:
Hunt (1993) noted that mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research after the publication of John Bowlby's studies.
Paraphrasing Examples
Original Source
Homeless individuals commonly come from families who are riddled with problems and marital disharmony, and are alienated from their parents. They have often been physically and even sexually abused, have relocated frequently, and many of them may be asked to leave home or are actually thrown out, or alternatively are placed in group homes or in foster care. They often have no one to care for them and no one knows them intimately.
Source from:
Rokach, A. (2005). The causes of loneliness in homeless youth. The Journal of Psychology , 139, 469-480.
Example: Incorrect Paraphrasing
The homeless come from families with problems. Frequently, they have been physically or sexually abused, or have lived in group homes. Usually no one cares for them or knows them intimately (Rokach, 2005).
Note : In this incorrect example the writing is too similar to the original source. The student only changed or removed a few words and has not phrased the ideas in a new way.
Example: Correct Paraphrasing
Many homeless experience isolation in part due to suffering from abuse or neglect during their childhood (Rokach, 2005).
Note : The example keeps the idea of the original writing but phrases it in a new way.
No Author and/or No Date
No Known Author:
Note that in most cases where a personal author is not named, a group author may be cited instead (eg. Statistics Canada). However, in certain cases, such as religious ancient texts, the author is unknown. Where you'd normally put the author's last name, instead use the first one, two, or three words from the title. Don't count initial articles like "A", "An" or "The". You should provide enough words to make it clear which work you're referring to from your References List.
If the title in the References list is in italics, italicize the words from the title in the in-text citation.
If you are citing an article, a chapter of a book or a page from a website, put the words in double quotation marks.
Capitalize the titles using title case (every major word is capitalized) even if the reference list entry uses sentence case (only first word is capitalized).
( Cell Biology , 2012, p. 157)
("Nursing," 2011, p. 9)
No Known Date of Publication :
Where you'd normally put the year of publication, instead use the letters "n.d.".
(Smith, n.d., p. 200)
In-Text Citation For Two or More Authors/Editors
| Number of Authors/Editors | First Time Paraphrased | Second and Subsequent Times Paraphrased | First Time Quoting | Second and Subsequent Times Quoting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two | (Case & Daristotle, 2011) | (Case & Daristotle, 2011) | (Case & Daristotle, 2011, p. 57) | (Case & Daristotle, 2011, p. 57) |
| Three or more | (Case et al., 2011) | (Case et al., 2011) | (Case et al., 2011, p. 57) | (Case et al., 2011, p. 57) |
In-Text Citation for Group or Corporate Authors
| Type of Group | First Time Paraphrased | Second and Subsequent Times Paraphrased | First Time Quoting | Second and Subsequent Times Quoting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups readily identified through abbreviations | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH, 2003) | (NIMH, 2003) | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH, 2003, p. 5) | (NIMH, 2003, p. 5) |
| Groups with no abbreviations | (University of Pittsburgh, 2005) | (University of Pittsburgh, 2005) | (University of Pittsburgh, 2005, p. 2) | (University of Pittsburgh, 2005, p. 2)
|
- << Previous: Quoting
- Next: Reference List & Sample Writing >>
- Last Updated: Jun 7, 2024 9:43 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.uwm.edu/c.php?g=1007936

ACAP LEARNING RESOURCES
Reference in APA 7
- Printable Guides & Sample Papers
- Headings & Page Order
- ACAP Presentation Requirements This link opens in a new window
- APA Style Guidelines, Blog & Socials
Paraphrasing
- Time Stamps, Verbatim, Transcripts & Personal Comms
- Secondary Sources
- Tables & Figures
- Missing, Same, Repeated, Multiples, Parts & Abbreviations
- Reference List Elements
- Formatting the Reference List
- DOIs, URLs & Hyperlinks
- Missing Information
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Edited, Republished & Translated Books
- Reference Works
- Diagnostic Manuals (DSM & ICD)
- Religious & Ancient Works
- Newspaper Articles
- Conferences & Theses
- Reports, Policies & Grey Literature
- YouTube & Other Streaming
- Podcasts, TV & Radio
- Transcripts
- Artwork & Images
- Social Media
- Legislation
- Standards & Patents
- Unpublished Works
- Statistics, Tests & Data Sets
- Generative Artificial Intelligence
Running text (Author, Date). Author (Date) running text.
Parenthetical Format . The citation can appear within or at the end of a sentence and includes the author and date separated by a comma. If at the end of a sentence a full stop is placed after the citation. Growth occurs at every stage of life (Newman & Newman, 2017). Case study research does not employ the scientific method (Barlow et al., 2017) although it is an important tool for qualitative researchers (Travers, 2001). Narrative Format . The author is used as part of the text, the date appears directly after the author in parentheses. If the date is used as a part of the text, just separate the author and date with a comma. As discussed by Newman and Newman (2017), growth occurs at every stage of life. In 2019, Hiscock et al. pointed out that half of Australian children and adolescents who experienced mental health issues did not receive professional treatment.
Common Examples
| Author Type | Parenthetical Citation | Narrative Citation |
|---|---|---|
| One author | (Hill, 2020). | Hill (2020). |
| Two authors | (Prochaska & Norcross, 2020). | Prochaska and Norcross (2020). |
| Three or more authors | (Geldard et al., 2017). | Geldard et al. (2017). |
| Group author with abbreviation First citation Subsequent citations |
(American Psychological Association [APA], 2020). (APA, 2020). |
American Psychological Association (APA, 2020). APA (2020). |
| Group author without abbreviation | (Department of Health, 2020). | Department of Health (2020). |
Long Paraphrases & Paragraphs
When paraphrasing or summarising using one source over several sentences or even a whole paragraph, cite the source in the first sentence. There is no need to cite the work again in this paragraph provided it is clear that this is the only source being paraphrased. The APA Style and Grammar Guidelines provide this example:
Velez et al. (2018) found that for women of color, sexism and racism in the workplace were associated with poor work and mental health outcomes, including job-related burnout, turnover intentions, and psychological distress. However, self-esteem, person–organization fit, and perceived organizational support mediated these effects. These findings underscore the importance of considering multiple forms of workplace discrimination in clinical practice and research with women of color, along with efforts to challenge and reduce such discrimination.
You must reintroduce the citation if the paraphrase continues across multiple paragraphs. If the paragraph or sentence contains information from multiple sources, then cite as often as required to make sure the source is clearly acknowledged. The APA Style and Grammar Guidelines provide this example:
Play therapists can experience many symptoms of impaired wellness, including emotional exhaustion or reduced ability to empathize with others (Elwood et al., 2011; Figley, 2002), disruption in personal relationships (Elwood et al., 2011; Robinson-Keilig, 2014), decreased satisfaction with work (Elwood et al., 2011), avoidance of particular situations (Figley, 2002; O’Halloran & Linton, 2000), and feelings or thoughts of helplessness (Elwood et al., 2011; Figley, 2002; O’Halloran & Linton, 2000).
Academic Writer Tutorial: Paraphrasing & Quoting
- << Previous: Citing In-text
- Next: Quotations >>
- Last Updated: Mar 13, 2024 1:57 PM
- URL: https://libguides.navitas.com/apa7
- 6th Edition Blog Home
- Blog Guidelines
- Subscribe to the Blog Feed
- APA Style Home
5 posts categorized "Paraphrasing"
March 03, 2015.
When and How to Include Page Numbers in APA Style Citations
Note: For examples and guidelines in seventh edition APA Style, see the following topic pages on the APA Style website: Quotations , Paraphrasing , and Direct Quotation of Material Without Page Numbers .
The examples in the following blog post are in sixth edition APA Style.
All APA Style in-text citations have two parts: the author and the date. Some in-text citations also include page numbers (or other location information when page numbers are not available, as with some online materials). This post describes when and how to include page numbers in APA Style for different kinds of citations as well as how to include the appropriate location information in lieu of page numbers when page numbers are not available.
Direct Quotations
A direct quotation reproduces the words of another writer verbatim and is displayed in quotation marks (if the quotation is fewer than 40 words) or as a block quotation (if the quotation is 40 words or more). When you include a direct quotation in a paper, include the author, date, and page number on which the quotation can be found (or other location information) in the citation.
| Research has found that “romantic partners maintain both biased and realistic views of a core relationship trait: physical attractiveness” (Solomon & Vazire, 2014, p. 524). Solomon and Vazire (2014) found that “romantic partners maintain both biased and realistic views of a core relationship trait: physical attractiveness” (p. 524). |
There are many ways to cite a direct quotation; see more examples here .
Paraphrases
A paraphrase restates someone else’s words in a new way. For example, you might put a sentence into your own words, or you might summarize what another author or set of authors found. When you include a paraphrase in a paper, you are required to include only the author and date in the citation. You are encouraged (but not required) to also provide the page number (or other location information) for a paraphrased citation when it would help the reader locate the relevant passage in a long or complex text (such as when you use only a short part of a book). The examples below show a citation for a paraphrase that includes the page number.
| Just as Sherlock Holmes investigates a case, psychologists must evaluate all the available data before making a deduction, lest they jump to an erroneous conclusion on the basis of insufficient evidence (Bram & Peebles, 2014, pp. 32–33). Bram and Peebles (2014) advocated for psychologists to evaluate all the available data before making a deduction, just as Sherlock Holmes investigates a case, lest they jump to an erroneous conclusion on the basis of insufficient evidence (pp. 32–33). |
There are many ways to paraphrase material; here are more examples and some advice .
How to Cite Material Without Page Numbers
If the cited material does not have page numbers (such as may occur with some e-books ) and you need them for an in-text citation, use any of the following location information instead:
- a paragraph number, if provided; alternatively, you can count paragraphs down from the beginning of the document;
- an overarching heading plus a paragraph number within that section; or
- an abbreviated heading (or the first few words of the heading) in quotation marks, in cases in which the heading is too unwieldy to cite in full, plus a paragraph number within that section.
| People planning for retirement need more than just money—they also “need to stockpile their emotional reserves” to ensure they have adequate support from family and friends (Chamberlin, 2014, para. 1). Chamberin (2014, para. 1) stated that people planning for retirement need more than just money—they also “need to stockpile their emotional reserves” to ensure they have adequate support from family and friends. |
For more on quoting and paraphrasing in APA Style, please see the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed., §§ 6.03–6.09).
| Bram, A. D., & Peebles, M. J. (2014). . Chamberlin, J. (2014, January). Retiring minds want to know. (1). Retrieved from Solomon, B. C., & Vazire, S. (2014). You are so beautiful . . . to me: Seeing beyond biases and achieving accuracy in romantic relationships. 516–528.
|
Posted by Chelsea Lee at 8:17 AM in Direct quotations , Paraphrasing | Permalink | Comments (60)
November 04, 2014
Lost in Translation: Citing Your Own Translations in APA Style
Dear Style Experts,
I am writing a paper in English for an English-speaking audience. However, I also speak French, and I read an article in French that I want to cite in my paper. I translated a quotation from the article from French into English. How do I format my translation of the quotation? Do I use quotation marks around it? Do I have to use the words “my translation” in there somewhere? Please help.
Translated Terry
Dear Translated Terry,
Your conundrum is a common one in this multilingual world. Luckily, the solution is quite simple: If you translated a passage from one language into another it is considered a paraphrase, not a direct quotation. Thus, to cite your translated material, all you need to do is include the author and date of the material in the in-text citation. We recommend (but do not require) that you also include the page number in the citation, because this will help any readers who do speak French to find the translated passage in the original. You should not use quotation marks around the material you translated, and you do not need to use the words “my translation” or anything like that. Here is an example:
| Original French passage: “Les femmes dans des activités masculines adoptaient des stéréotypes masculins” (Doutre, 2014, p. 332). |
| Translated quotation that appeared in the paper: Women working in masculine fields adopted masculine stereotypes (Doutre, 2014, p. 332). |
In the reference list, provide the citation for the work in its original language. Also provide an English translation of the title of the work in square brackets after the foreign-language title, without italics.
Reference list entry:
| Doutre, É. (2014). Mixité de genre et de métiers: Conséquences identitaires et relations de travail [Mixture of gender and trades: Consequences for identity and working relationships]. 327–336. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0036218 |
Why Is the Translation Considered a Paraphrase?
You may wonder why your translation is considered a paraphrase rather than a direct quotation. That’s because translation is both an art and a science—languages do not have perfect correspondences where every word and phrase matches up with a foreign equivalent, though of course some cases come closer than others. Even in the example passage above I considered how to translate “Les femmes dans des activités masculines”—taken word for word I might have written “Women in masculine activities,” but I thought “Women working in masculine fields” better conveyed the actual meaning, which relates to women working in male-dominated occupations.
Nevertheless, because we can't codify how exact any given translation is, it would be inappropriate to put quotation marks around the translated words. In fact, in undertaking the translation yourself you have literally put the author’s words into your own words, which is the definition of a paraphrase.
Citing a Published Translation
Finally, note that citing a translation you made is different than citing a published translation someone else made. If you read a work in translation and you used a direct quotation from it in your paper, you would put quotation marks around the quoted passage just as for any other direct quotation citation. Although the work has been translated, it exists in a distinct, retrievable form. Likewise, in the reference list you would write an entry for the translated version of the work .
I hope this helps you cite your own translations in APA Style.
—Chelsea Lee
Posted by Chelsea Lee at 9:22 AM in Common references , Direct quotations , How-to , Paraphrasing , Translations | Permalink | Comments (24)
July 10, 2014
Does APA Style Use Ibid. ?
By David Becker
Dear APA Style Experts,
When should I use ibid. in my research paper? I want to cite the same source multiple times in a row, but I’m not sure how. Please help!
Dear Brann,
Ibid. is one of several topics not covered in the Publication Manual because it isn’t used in APA Style. Other styles that document sources with footnotes or endnotes use ibid. to point to a source that was cited in a preceding note. APA Style, however, consistently uses the author–date format to identify an idea’s origin.
When repeatedly referring to the same source, it’s not always necessary to include a parenthetical citation at the end of every paraphrased sentence , as long as the narrative plainly indicates where the information is coming from. Even a direct quotation may not require a full parenthetical citation in this case—you can vary your citation style . If you’re not sure whether your paper clearly shows that you’re drawing multiple thoughts from one source, just ask your instructor, a classmate, or someone at your school’s writing center to give it a quick read. One of the most valuable resources in any form of writing is a second pair of eyes!
I hope this post answered your question, Brann! You can also turn to pages 174–175 of the Publication Manual for examples that show how to integrate citations into the narrative and when to include the publication date . Also be sure to check out one of our earlier posts that briefly reviews how to create in-text citations . And, as always, feel free to comment on this post, leave us a note on Twitter or Facebook , or contact us directly about any questions you may have.
Posted by David Becker at 3:55 PM in Direct quotations , In-text citations , Paraphrasing | Permalink | Comments (1)
April 04, 2013
When to Include the Year in Citations Appearing More Than Once in a Paragraph
by Tyler Krupa
You may already know that references in APA Style are cited in text with an author–date system (e.g., Smith, 2012). But do you know when to include the year of publication when one of your citations appears more than once in a paragraph? Getting it right is simple as long as you remember the following two guidelines:
1. All parenthetical citations (i.e., citations in which both the author name and publication date are enclosed within parentheses) should include the year, regardless of how often they appear in a paragraph.
2. When the name of the author is part of the narrative and appears outside of parentheses , after the first citation in each paragraph you need not include the year in subsequent nonparenthetical citations as long as the study cannot be confused with other studies in the article (see p. 174 in the sixth edition of the Publication Manual ).
To help illustrate these guidelines, let’s look at a few examples that correctly show when to include the year in citations appearing more than once in a paragraph:
| described two separate but linked epidemics. . . . distinguished the HIV (viral) epidemic from the subsequent AIDS (disease) epidemic, foreseeing the ultimate convergence of preventing the spread of the virus and managing the disease it causes. . . . also discussed a third epidemic . . . . This third epidemic is as much a part of the pathology of AIDS as the virus itself . Socioeconomic status (SES) and chronic diseases rather consistently fall on a gradient, where those of relatively lower SES have poorer health and are more often afflicted by multiple diseases than those above them on the SES ladder . . . . offered a framework to explain the major pathways by which SES can influence health outcomes. . . . The model is developmental, illustrating individual, social, and structural influences on disease over the lifespan . |
We hope these examples clear up this point of possible uncertainty. Still have questions? Leave us a comment.
Posted by Timothy McAdoo at 1:51 PM in How-to , In-text citations , Paraphrasing | Permalink | Comments (23)
Technorati Tags : author name , citations , paragraph , parentheses , year
March 18, 2011
Citing Paraphrased Work in APA Style
As the Publication Manual notes, citing your sources is imperative: “Whether paraphrasing, quoting an author directly, or describing an idea that influenced your work, you must credit the source” (p. 170). But, we are sometimes asked how a writer can properly and clearly attribute multiple ideas within a paragraph yet maintain a readable and interesting text. It’s a challenge! If you include a citation only at the end of the paragraph, the reader won’t know how many of the ideas in the previous sentences you are attributing to the cited author. But, including the citation at the end of each sentence, an absolutely clear and correct approach, can become redundant:
| The cross-pollination and fusion of musical genres over the last 2 decades has exposed children to a diversity of musical styles (Viglione, 2010). Technology has also made possible the distribution and sharing of music in exciting new ways (Viglione, 2010). Music is shared through social media sites, analyzed and tailored for the individual listener via sites like Pandora, and simply given away by musicians on their websites (Viglione, 2010). As a result, in the future, children will likely develop eclectic musical tastes early and expect a diversity of musical styles at younger and younger ages (Viglione, 2010). |
The paragraph above clearly attributes the work of Viglione (2010), but imagine a 20-page literature review written in this style! Pages 15–16 of the Publication Manual show an example of how to paraphrase multiple ideas without this redundancy. Can you rewrite the paragraph above in a way that avoids redundancy but maintains the attribution of all of the ideas? Submit your suggestions in the comments section! There are many ways to improve this paragraph, so we won’t post a “winner,” but we will follow up with comments and commendations on the suggested rewrites!
Posted by Timothy McAdoo at 11:05 AM in Common references , How-to , In-text citations , Paraphrasing , References | Permalink | Comments (46)
Technorati Tags : APA Style
For seventh edition guidelines, visit the seventh edition APA Style blog . This search includes only sixth edition blog archive results:
ABOUT THE 6TH EDITION BLOG ARCHIVE
APA Style FAQs
- Abbreviations
- Advance online publication
- Announcements
- Author names
- Best of Blog
- Bias-free language
- Capitalization
- Common references
- Computer tips
- Digital Object Identifier (DOI)
- Direct quotations
- ebooks/Kindle
- Electronic references
- Grammar and usage
- Hyphenation
- In-text citations
- Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS)
- Journal articles
- Movies and TV
- Numbers and metrication
- Paraphrasing
- Personal communications
- Principles of good writing
- Publication Manual help
- Publication process
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Junction
- Reference list
- Research participants
- Running heads
- Social media
- Tables and figures
- Tests and measures
- Translations
Recent Posts
Recent comments.
- Chelsea Lee on Hyphenation Station: The Hyphenation of Prefixes in APA Style
- David Becker on How to Cite Edition, Volume, and Page Numbers for Books
- APA Style on The Seventh Edition of the Publication Manual Is Available for Preorder!
- Soham_DB on How to Cite Edition, Volume, and Page Numbers for Books
- Soham_DB on How to Quote a Foreign-Language Source and Its Translation
- Chelsea Lee on How to Quote a Foreign-Language Source and Its Translation
- D on The Seventh Edition of the Publication Manual Is Available for Preorder!
- Oliwiakopinska on Pluralize Numbers and Abbreviations Without Apostrophes
- David Becker on Pluralize Numbers and Abbreviations Without Apostrophes
Twitter Updates
Encyclopedia for Writers
Writing with ai, apa paraphrase.
- © 2023 by Jennifer Janechek - University of Iowa
Table of Contents
How should a paraphrased passage be cited?
When paraphrasing a passage, it is essential to express the ideas of the author in your own original words; however, the author’s message and meaning should always be preserved.
Charges of plagiarism can be avoided by including the proper citation of the work you are drawing from in your paraphrase. The APA requires a paraphrase to include the author’s last name and the work’s year of publication, but also suggests that the page number of the original text be included.
Let’s look at an example of a cited paraphrase:
Original text: “A yellow flower is yellow because it reflects yellow light and absorbs other wavelengths. The red glass of a stained glass window is red because it transmits red light and absorbs other wavelengths. The process by which we perceive the colours of natural objects around us can therefore be described as a ‘subtractive’ process” (Pender, 1998, p. 14). [1]
Paraphrase: Pender explains that through subtractive process , humans see the color of objects based on the wavelengths of light that are absorbed by each object (Pender, 1998, p. 14). [1]
Note: The paraphrase maintains the ideas of the original passage while expressing the message in a new voice. The original author is also cited properly.
How should a summarized passage or work be cited?
When summarizing a passage or work from another writer, briefly outline in your own original words the major ideas presented in the source material. As brevity is the key feature of a summary, it is essential to express the main concepts of the original passage in as concise a manner as possible. Consider using a summary—rather than a short or block quotation—when preserving the original wording of the source material is not necessary for the reader to understand the ideas under discussion.
Let’s look at an example of a cited summary:
Original text: “In their everyday life, people generally assume that they see the world around them the way it really is. When camping in Colorado, hikers believe they see the horizon as dotted with snow-covered mountaintops. When laying on the beach in North Carolina, sunbathers believe they see pelicans flying above the breaking waves. And these people would nearly always be right. Indeed, it is difficult to imagine not believing that the sights and sounds delivered to conscious awareness by perceptual systems are accurate renderings of the outside world. It would be difficult to know how to act if one could not trust one’s senses to accurately report what the world outside is like” (Balcetis, 2010, p. 77). [2]
Summary: In Social Psychology of Visual Perception , Balcetis (2010) argues that because humans rely on the sensory information received from their body, they form preconceived beliefs about their surroundings that manifest as imaginary visual occurrences (p. 77). [2]
Note: The summary maintains the ideas of the original passage while concisely expressing its main concepts. The original author is also cited properly.
How should multiple sources be cited in a single parenthetical reference?
If multiple works need to be cited in the same set of parentheses, simply arrange them in alphabetical order by the author’s last names, or the order in which they would be listed in the References page. Use a semicolon to separate each work from the next one.
Let’s look at an example of multiple authors being cited:
In the past thirty years, Parkinson’s disease has been written about extensively by recognized figures in the field (Dorros, 1989; Duvoisin, 1991; Hauser & Zesiewicz, 1996). [3][4][5]
Note: This example includes the in-text citations of three works arranged in alphabetical order by authors’ names, separated by semi-colons, and enclosed in parentheses.
- Formatting In-text Citations (APA)
[1] Pender, K. (1998). Digital colour in graphic design . Burlington, VT: Elsevier Science & Technology.
[2] Balcetis, E. (2010). Social psychology of visual perception . Hoboken, NJ: Taylor & Francis.
[3] Dorros, S. (1989). Parkinson’s: A patient’s view . Cabin John, MD: Seven Locks Press.
[4] Duvoisin, R. C. (1991). Parkinson’s disease: A guide for patient and family . New York, NY: Raven Press.
[5] Hauser, R. A., & Zesiewicz, T. A. (1996). Parkinson’s disease: Questions and answers . Coral Springs, FL: Merit.
The Elements of Style

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Recommended

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Structured Revision – How to Revise Your Work

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority & Credibility – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Research, Speech & Writing

Citation Guide – Learn How to Cite Sources in Academic and Professional Writing

Page Design – How to Design Messages for Maximum Impact
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - How to Differentiate Quality Information from Misinformation & Rhetrickery
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. You need to be strategic about how you consume and use information in order to thrive,...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

- Essay Topic Generator
- Essay Grader
- Reference Finder
- AI Outline Generator
- Paragraph Expander
- Essay Expander
- Literature Review Generator
- Thesis Generator
- Text Editing Tools
- AI Rewording Tool
- AI Sentence Rewriter
- AI Article Spinner
- AI Grammar Checker
- Spell Checker
- PDF Spell Check
- Paragraph Checker
- Free AI Essay Writer
- Paraphraser
- Grammar Checker
- Citation Generator
- Plagiarism Checker
- AI Detector
- AI Essay Checker
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- AI Writing Guides
- AI Detection Guides
- Citation Guides
- Grammar Guides
- Paraphrasing Guides
- Plagiarism Guides
- Summary Writing Guides
- STEM Guides
- Humanities Guides
- Language Learning Guides
- Coding Guides
- Top Lists and Recommendations
- AI Detectors
- AI Writing Services
- Coding Homework Help
- Citation Generators
- Editing Websites
- Essay Writing Websites
- Language Learning Websites
- Math Solvers
- Paraphrasers
- Plagiarism Checkers
- Reference Finders
- Spell Checkers
- Summarizers
- Tutoring Websites
- Essay Checkers
- Essay Topic Finders
Most Popular
Spooktacular halloween writing prompts that will blow your gourd clean off, how to quote a poem in an essay, enjoy the most creative halloween writing activities.
10 days ago
Essay Topics on Black Friday History for Students
How to write a why us essay, how to paraphrase in apa.
freepik.com

Paraphrasing is a fundamental skill in academic writing, especially when adhering to specific citation styles like APA (American Psychological Association). In this article, we will explore the nuances of paraphrasing in APA, understand the distinction between citations and paraphrases, and uncover valuable tips to ensure your paraphrased content is not flagged as plagiarism.
What Is APA Citation Style?
APA citation style is widely used in various academic disciplines, including psychology, social sciences, and education. It provides a standardized format for citing sources in research papers, ensuring consistency, credibility, and ease of comprehension for readers. Proper APA citation style is essential for acknowledging the work of others and avoiding plagiarism .

What Is the Difference Between a Citation and a Paraphrase?
Citations and paraphrases serve distinct purposes in academic writing. A citation is a direct reference to a source, providing readers with the exact location of the quoted or paraphrased material. In contrast, a paraphrase involves restating someone else’s ideas or information in your own words, preserving the original meaning while avoiding verbatim repetition.
How to Paraphrase in APA Examples
Let’s look at several APA paraphrasing examples to know exactly what we’ve dealing with.

Examples of Citing Paraphrased Information in APA at the Beginning of a Sentence
| Paraphrased Information at the Beginning of a Sentence | Description |
|---|---|
| According to Williams (2021), an extensive examination of climate change was undertaken. | In this example, the author’s name, Williams, is mentioned in the text itself, followed by the publication year in parentheses. |
| The global impact of climate change is a matter of great concern (Terrence, 2019). | Here, the author’s name and publication year are enclosed in parentheses at the end of the paraphrased sentence. |
| Immediate action is underscored in climate change research (Smith & Johnson, 2023). | In this case, two authors, Smith and Johnson, are cited within the parentheses, representing a paraphrased statement from their research. |
Examples of Citing Paraphrased Information in APA in the Middle of a Sentence
| Sentence with Paraphrased Information and Citation | Description |
|---|---|
| Recent studies (Webkin, 2022) have shown a significant decline in biodiversity. | In this example, the author’s last name, Webkin, and the publication year, 2022, are integrated into the middle of the sentence, providing context for the research. |
| The impact of technology on daily life has been extensively explored (Gregson & Lee, 2019). | Here, two authors, Gregson and Lee, are cited within the sentence, emphasizing the significance of their research within the context of the sentence. |
| According to recent findings (Diaz et al., 2021), the link between stress and health outcomes is well-established. | In this case, multiple authors are represented by “Diaz et al.” in the middle of the sentence, indicating the collective research effort. |
Another way to cite your sources is to mention them at the end of the sentence.
| Sentence with Paraphrased Information and Citation | Description |
|---|---|
| The impact of climate change on coastal ecosystems is evident (Scholtz, 2018). | In this example, the author’s last name, Scholtz, and the publication year, 2018, are placed at the end of the sentence to attribute the information. |
| Social media has transformed communication patterns (Oishi & Serene, 2021). | Here, two authors, Oishi and Serene, are cited at the sentence’s end, acknowledging their research’s contribution to the statement. |
| The role of genetics in human behavior has been extensively researched (Sandy et al., 2020). | In this case, multiple authors are represented by “Sandy et al.” at the end of the sentence, crediting their collective work. |
Here’s how you can paraphrase the original information into your work without it being considered plagiarism.
Original text : The complexity of disaster experience calls for considerations at many different levels of inquiry: environmental, psychological, social, political, and cultural. Yet, the crux of disaster experience is the dynamic interplay of environmental challenges and losses embedded within collective processes of mutual exchanges of aid and support. Hence, the featured research findings are organized along the three most distinct operational facets of an all-embracing construct of social support: received social support (e.g. ‘being actually helped by others in times of need’), perceived social support (e.g. ‘subjective appraisals of being reliably connected to others’), and social embeddedness(e.g. ‘types and frequency of interpersonal and community connections’). Source: Kaniasty, K. (2019). Social support, interpersonal, and community dynamics following disasters caused by natural hazards. Current Opinion in Psychology . doi:10.1016/j.copsyc.2019.07.026

Tips for Correct Paraphrasing
Effective paraphrasing not only demonstrates your understanding of the source material but also safeguards against plagiarism. Here are essential tips to master the art of paraphrasing in APA.
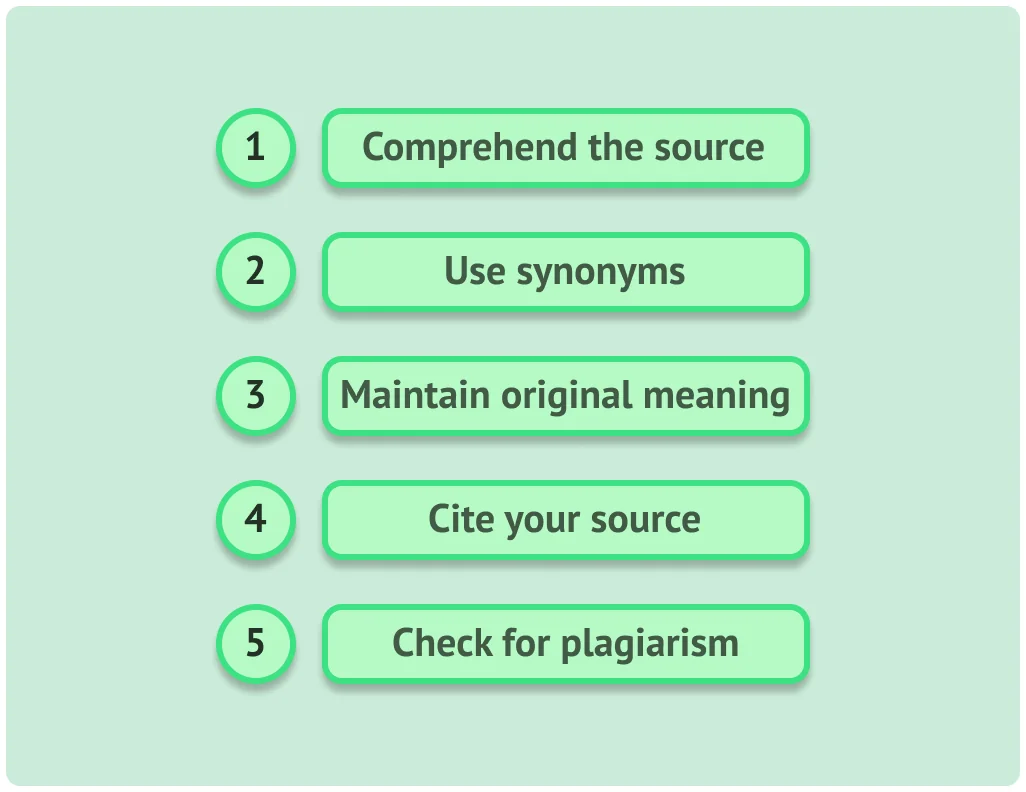
Before embarking on the paraphrasing journey, it is crucial to have a deep understanding of the source material. Delve into the text, dissecting complex ideas and concepts. Simplify intricate passages in your mind to grasp the core message. This comprehension forms the foundation of effective paraphrasing.
Paraphrasing involves substituting words with synonyms and reorganizing sentence structure while retaining the original meaning. A thesaurus can be a valuable tool in finding appropriate synonyms . By reshaping sentences and words creatively, you can convey the same information without copying the source verbatim.
While rephrasing, the core idea and intention of the source must remain intact. It is essential to preserve the author’s message and avoid any distortions. Ensure that your paraphrase accurately reflects the source’s meaning, providing a fresh perspective without altering the content’s essence.
Even in the process of paraphrasing, always acknowledge the source. In-text citations following APA guidelines are necessary. Include the author’s last name and the publication year to provide clear attribution . This practice not only maintains academic integrity but also allows readers to trace the original source.
Utilize plagiarism detection tools as a final step to verify your paraphrased content. These tools help ensure that your paraphrased text does not unintentionally resemble the original source too closely. Thoroughly checking for similarities and making necessary adjustments guarantees that your work remains free from plagiarism concerns.
Paraphrasing in APA is an essential skill for any student or researcher. By understanding the intricacies of APA citation style, distinguishing between citations and paraphrases, and following our tips for correct paraphrasing, you can ensure your academic work is both credible and free from plagiarism. Mastering this skill empowers you to incorporate the ideas of others seamlessly while maintaining the integrity of your own writing.
How to properly paraphrase in APA style?
To paraphrase effectively in APA style, read and understand the original text, then express the ideas in your own words while retaining the original meaning . Always provide an in-text citation with the author’s last name and publication year, even when paraphrasing. Ensure the citation is placed correctly within the sentence.
What are the APA citation guidelines for paraphrasing?
When paraphrasing in APA style, include the author’s last name and the publication year in parentheses at the end of the paraphrased sentence. If the author’s name is mentioned in the text, include the year in parentheses immediately afterward.
Can I use a paraphrasing tool for APA style?
Yes, of course you can . Ine of such tools is AcademicHelp’s Paraphraser, which is specifically tailored in accordance to student needs. However, it’s essential to proofread your text just in case. It’s necessary to understand the content and then manually compare it to APA guidelines to ensure accuracy.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.
Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More from Paraphrasing Guides

APA Paraphrasing

Why Is Paraphrasing Important?

Do Paraphrases Need Quotation Marks
Remember Me
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email

- Joyner Library
- Laupus Health Sciences Library
- Music Library
- Digital Collections
- Special Collections
- North Carolina Collection
- Teaching Resources
- The ScholarShip Institutional Repository
- Country Doctor Museum
APA Citation Style, 7th Edition: In-Text Citations & Paraphrasing
- APA 6/7 Comparison Guide
- New & Notable Changes
- Student Paper Layout
- Journal Article with One Author
- Journal Article with Two Authors
- Journal Article with Three or more Authors
- Help?! I can't find the DOI
- One Author/Editor
- Two Authors/Editors
- Chapter in a Book
- Electronic Books
- Canvas Posts & Class Discussion Boards
- Datasets, Software, & Tests
- Dissertations & Thesis
- Government Websites & Publications, & Gray Literature
- Infographic, Powerpoint, or other visual works
- Legislative (US & State House & Senate) Bills
- Podcast or other audio works
- Social Media Posts
- StatPearls, UpToDate, DynaMedex
- YouTube or other streaming video
- Citing the use of AI
- Interviews & Emails
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Posters & Conference Sessions
- Photographs, Tables, & PDF's
- In-Text Citations & Paraphrasing
- References Page
- Free APA 7th edition Resources, Handouts, & Tutorials
When do I use in-text citations?
When should you add in-text citations in your paper .
There are several rules of thumb you can follow to make sure that you are citing your paper correctly in APA 7 format.
- Think of your paper broken up into paragraphs. When you start a paragraph, the first time you add a sentence that has been paraphrased from a reference -> that's when you need to add an in-text citation.
- Continue writing your paragraph, you do NOT need to add another in-text citation until: 1) You are paraphrasing from a NEW source, which means you need to cite NEW information OR 2) You need to cite a DIRECT quote, which includes a page number, paragraph number or Section title.
- Important to remember : You DO NOT need to add an in-text citation after EVERY sentence of your paragraph.

What do in-text citations look like?
In-text citation styles: .
| (Forbes, 2020) | Forbes (2020) stated... | |
| (Bennet & Miller, 2019) | Bennet and Miller (2019) concluded that... | |
| (Jones et al., 2020) | Jones et al. (2020) shared two different... | |
| (East Carolina University, 2020) | East Carolina University (2020) found... |
Let's look at these examples if they were written in text:
An example with 1 author:
Parenthetical citation: Following American Psychological Association (APA) style guidelines will help you to cultivate your own unique academic voice as an expert in your field (Forbes, 2020).
Narrative citation : Forbes (2020) shared that by following American Psychological Association (APA) guidelines, students would learn to find their own voice as experts in the field of nursing.
An example with 2 authors:
Parenthetical citation: Research on the use of progressive muscle relaxation for stress reduction has demonstrated the efficacy of the method (Bennett & Miller, 2019).
Narrative citation: As shared by Bennett and Miller (2019), research on the use of progressive muscle relaxation for stress reduction has demonstrated the efficacy of the method.
An example with 3 authors:
Parenthetical citation: Guided imagery has also been shown to reduce stress, length of hospital stay, and symptoms related to medical and psychological conditions (Jones et al., 2020).
Narrative citation: Jones et al. (2020) shared that guided imagery has also been shown to reduce stress, length of hospital stay, and symptoms related to medical and psychological conditions.
An example with a group/corporate author:
Parenthetical citation: Dr. Philip G. Rogers, senior vice president at the American Council on Education, was recently elected as the newest chancellor of the university (East Carolina University, 2020).
Narrative citation: Recently shared on the East Carolina University (2020) website, Dr. Philip G. Rogers, senior vice president at the American Council on Education, was elected as the newest chancellor.
Tips on Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing is recreating someone else's ideas into your own words & thoughts, without changing the original meaning (gahan, 2020). .
Here are some best practices when you are paraphrasing:
- How do I learn to paraphrase? IF you are thoroughly reading and researching articles or book chapters for a paper, you will start to take notes in your own words . Those notes are the beginning of paraphrased information.
- Read the original information, PUT IT AWAY, then rewrite the ideas in your own words . This is hard to do at first, it takes practice, but this is how you start to paraphrase.
- It's usually better to paraphrase, than to use too many direct quotes.
- When you start to paraphrase, cite your source.
- Make sure not to use language that is TOO close to the original, so that you are not committing plagiarism.
- Use theasaurus.com to help you come up with like/similar phrases if you are struggling.
- Paraphrasing (vs. using direct quotes) is important because it shows that YOU ACTUALLY UNDERSTAND the information you are reading.
- Paraphrasing ALLOWS YOUR VOICE to be prevalent in your writing.
- The best time to use direct quotes is when you need to give an exact definition, provide specific evidence, or if you need to use the original writer's terminology.
- BEST PRACTICE PER PARAGRAPH: On your 1st paraphrase of a source, CITE IT. There is no need to add another in-text citation until you use a different source, OR, until you use a direct quote.
References :
Gahan, C. (2020, October 15). How to paraphrase sources . Scribbr.com . https://tinyurl.com/y7ssxc6g
Citing Direct Quotes
When should i use a direct quote in my paper .
Direct quotes should only be used occasionally:
- When you need to share an exact definition
- When you want to provide specific evidence or information that cannot be paraphrased
- When you want to use the original writer's terminology
From: https://americanlibrariesmagazine.org/whaddyamean/
Definitions of direct quotes:
| , around the quote, are incorporated into the text of the paper. | (Shayden, 2016, p. 202) | |
| (by indenting 0.5" or 1 tab) beneath the text of the paragraph. | (Miller et al., 2016, p. 136) | |
| , therefore you need a different way to cite the information for a direct quote. There are two ways to do this: | (Jones, 2014, para. 4) (Scotts, 2019, Resources section) |
- Western Oregon University's APA Guidelines on Direct Quotes This is an excellent quick tutorial on how to format direct quotes in APA 7th edition. Bookmark this page for future reference!
Carrie Forbes, MLS

Chat with a Librarian

Chat with a librarian is available during Laupus Library's open hours .
Need to contact a specific librarian? Find your liaison.
Call us: 1-888-820-0522 (toll free)
252-744-2230
Text us: 252-303-2343
- << Previous: Photographs, Tables, & PDF's
- Next: References Page >>
- Last Updated: Jul 26, 2024 2:47 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ecu.edu/APA7

- Hamersly Library
APA Style Guide 7th Edition
- Summary/Paraphrase
- About This Guide
- Direct Quote
- Block Quote
- Indirect Quote
- Tables/Graphs/Images
- Personal Communications
- Book/E-book
- Journal Article
- Website/Webpage
- Social Media
- Conference Papers/Presentations
- Thesis and Dissertations
- Video/Film/TV
- Music/Audio
- Visual Works
- Student Paper Guidelines
- Professional Paper Guidelines
- Creating Original Tables, Graphs, and Images
- Additional Help
General Guidelines for Paraphrasing and Summarizing
- Paraphrasing is when you put a passage or idea from another work into your own words.
- A paraphrased passage is generally shorter and more condensed than the original.
- You can cite your information as part of the sentence (called a narrative citation) or at the end in parentheses (known as a parenthetical citation).
- Summarizing is very similar to paraphrasing in that it also involves putting someone else’s ideas into your own words in order to condense the material.
- A summary includes only the main points and/or ideas in a longer passage or entire work.
- If you have two or more authors, use the word 'and' for narrative citations and the ampersand '&' for parenthetical citations.
- If you have three or more authors, use 'et al.' after the first authors last name to indicated there are additional authors.
- You only include the author/year from the article your are summarizing. You do not need to include page numbers or section identification.
- If you are citing multiple works parenthetically, place the citations in alphabetical order separated by semicolons.
Narrative Paraphrasing/Summarizing
Single Author: Simmons (2019) notes that teachers need to use clear body language including using good posture and eye contact when giving directions.
Two Authors: Orben and Przybylski (2019) determined that half of the participants in recent studies overestimated how much time they spend on the internet and a quarter of the participants underestimate it.
Three or More Authors: Larson et al. (2019) pointed out middle school students reported significant less time spent outdoors in nature and more time on screens than their parents reported they did.
Parenthetical Paraphrasing/Summarizing
Single Author: Teachers need to use clear body language including using good posture and eye contact when giving directions (Simmons, 2019).
Two Authors: H alf of the participants in recent studies overestimated how much time they spend on the internet and a quarter of the participants underestimate it (Orben & Przybylski, 2019).
Three or More Authors: Middle school students reported significant less time spent outdoors in nature and more time on screens than their parents reported they did ( Larson et al., 2019).
Parenthetical Summary With Multiple Sources
Behavior-specific praise and adherence to schedule and routines are two classroom management practices that can increase academic engagement and improve classroom management (Collier-Meek et al., 2019; O’Hanley & Jones, 2020; Simmons, 2019).
- << Previous: Indirect Quote
- Next: Tables/Graphs/Images >>
- Last Updated: Jul 16, 2021 2:43 PM
- URL: https://research.wou.edu/APA7

APA Style 7th Edition
- Advertisements
- Books & eBooks
- Book Reviews
- Class Notes, Class Lectures and Presentations
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Charts, Graphs, Maps & Tables
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Personal Communication (Interviews & Emails)
- Social Media
- Videos & DVDs
- What is a DOI?
- When Creating Digital Assignments
- When Information is Missing
- Works Cited in Another Source
- In-Text Citation Components
Paraphrasing
- Paper Formatting
- Citation Basics
- Reference List and Sample Papers
- Annotated Bibliography
- Academic Writer
- Plagiarism & Citations
When you write information from a source in your own words, cite the source by adding an in-text citation at the end of the paraphrased portion as follows:
Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt, 1993).
Note : If you refer to the author's name in a sentence you do not have to include the name again as part of your in-text citation, instead include the year of publication following his/her name:
Hunt (1993) noted that mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research after the publication of John Bowlby's studies.
Paraphrasing Examples
Original Source
Homeless individuals commonly come from families who are riddled with problems and marital disharmony, and are alienated from their parents. They have often been physically and even sexually abused, have relocated frequently, and many of them may be asked to leave home or are actually thrown out, or alternatively are placed in group homes or in foster care. They often have no one to care for them and no one knows them intimately.
Source from:
Rokach, A. (2005). The causes of loneliness in homeless youth. The Journal of Psychology , 139, 469-480.
Example: Incorrect Paraphrasing
The homeless come from families with problems. Frequently, they have been physically or sexually abused, or have lived in group homes. Usually no one cares for them or knows them intimately (Rokach, 2005).
Note : In this incorrect example the writing is too similar to the original source. The student only changed or removed a few words and has not phrased the ideas in a new way.
Example: Correct Paraphrasing
Many homeless experience isolation in part due to suffering from abuse or neglect during their childhood (Rokach, 2005).
Note : The example keeps the idea of the original writing but phrases it in a new way.
In-Text Citation For Two or More Authors/Editors
| Number of Authors/Editors | First Time Paraphrased | Second and Subsequent Times Paraphrased | First Time Quoting | Second and Subsequent Times Quoting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Case & Daristotle, 2011) | (Case & Daristotle, 2011) | (Case & Daristotle, 2011, p. 57) | (Case & Daristotle, 2011, p. 57) | |
| (Case et al., 2011) | (Case et al., 2011) | (Case et al., 2011, p. 57) | (Case et al., 2011, p. 57) |
In-Text Citation for Group or Corporate Authors
| Type of Group | First Time Paraphrased | Second and Subsequent Times Paraphrased | First Time Quoting | Second and Subsequent Times Quoting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH, 2003) | (NIMH, 2003) | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH, 2003, p. 5) | (NIMH, 2003, p. 5) | |
| (University of Pittsburgh, 2005) | (University of Pittsburgh, 2005) | (University of Pittsburgh, 2005, p. 2) | (University of Pittsburgh, 2005, p. 2) |
No Author and/or No Date
No Known Author:
Note that in most cases where a personal author is not named, a group author may be cited instead (eg. Statistics Canada). However, in certain cases, such as religious ancient texts, the author is unknown. Where you'd normally put the author's last name, instead use the first one, two, or three words from the title. Don't count initial articles like "A", "An" or "The". You should provide enough words to make it clear which work you're referring to from your References List.
If the title in the References list is in italics, italicize the words from the title in the in-text citation.
If you are citing an article, a chapter of a book or a page from a website, put the words in double quotation marks.
Capitalize the titles using title case (every major word is capitalized) even if the reference list entry uses sentence case (only first word is capitalized).
( Cell Biology , 2012, p. 157)
("Nursing," 2011, p. 9)
No Known Date of Publication :
Where you'd normally put the year of publication, instead use the letters "n.d.".
(Smith, n.d., p. 200)
- << Previous: Quoting
- Next: Formatting >>
- Last Updated: Mar 4, 2024 1:55 PM
- URL: https://guides.fscj.edu/APAStyle7

- Research Guides
- A-Z Database List
- Library Home
APA 7th Edition Citation Guide
- Formatting Essays
- Paraphrase and Summary
What Are Paraphrase and Summary?
Paraphrase (narrative citation), summary (parenthetical citation).
- Bibliographic Citations
- Sources with Multiple Authors
- Sources with No Author, Date, Title or Page Numbers
- Journal Articles
- Magazine and Newspaper Articles
- Reference Articles, Encyclopedia and Dictionary Entries
- Books and eBooks
- Conference Proceedings and Presentations
- Dissertations and Theses
- Films, Video and Audio
- Government Documents, Non-Profit and Corporate Reports
- Images and Advertisements
- Personal Communications (E-mails, Interviews, and etc.)
- Religious Texts
- Social Media
- Statutes, Legal Documents and the Constitution
- Avoiding Plagiarism
Sara Carman , Librarian
Call: 320-629-5169

Laurie Jorgensen , Library Technologist
Call: 320-629-5145
24/7 Chat help is available!
Paraphrase and Summary:
- Incorporate a portion of the source into your essay by conveying its meaning in your own words.
- Paraphrase aims to replicate all of the ideas of the source passage, while summary aims to express only its main point(s).
- Are introduced by a signal phrase, incorporating the source passage into the flow of the essay. Typically, the signal phrase will indicate to the reader something about the source of the paraphrase.
- End with a citation indicating the author of the source and, in APA style, the year it was published.
When do I use Paraphrase and Summary?
- When you want to call attention to what a source says, but how it says it is not important.
- When you only want to convey a source's main idea in a short amount of time.
- Use paraphrase and summary frequently. APA is designed for the social and health sciences, which typically have less need for direct quotation than the humanities.
How Do I Paraphrase/Summarize a Source?
- Read and understand the source.
- Identify the main points and supporting information of the portions you want to paraphrase/summarize.
- Re-write those portions in your own words, being careful not to use similar phrasing of sentence structure.
- Does it properly convey the meaning of the original?
- Are the sentence structure and phrasing too similar?
The struggle to fill nursing positions is different from the effort to add to the physician workforce. One main reason: there are not enough faculty to teach incoming nursing students. Either faculty are leaving due to retirement -- like their counterparts in health-care settings, they too are aging – or they’re gaining higher salaries elsewhere in practice settings other than teaching.
Moore, M. (2015, June 5). The nursing shortage and the doctor shortage are two very different things. The Washington Post . https://www.washingtonpost.com
Paraphrase:

- << Previous: Quotation
- Next: Bibliographic Citations >>
- Last Updated: Feb 20, 2024 5:50 PM
- URL: https://pine.libguides.com/APA7Guide

APA Citation Guide (7th edition) : Paraphrasing
- What Kind of Source Is This?
- Advertisements
- Books & eBooks
- Book Reviews
- Class Handouts, Presentations, and Readings
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Charts, Graphs, Maps & Tables
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Personal Communication (Interviews, Emails)
- Social Media
- Videos & DVDs
Paraphrasing
- Works Cited in Another Source
- No Author, No Date etc.
- Sample Paper, Reference List & Annotated Bibliography
- Powerpoint Presentations
On This Page
Paraphrasing examples.
- In-Text Citation for More Than One Author
In-Text Citation for Group or Corporate Authors
No author and/or no date.
When you write information from a source in your own words, cite the source by adding an in-text citation at the end of the paraphrased portion as follows:
Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt, 1993).
Note : If you refer to the author's name in a sentence you do not have to include the name again as part of your in-text citation, instead include the year of publication following his/her name:
Hunt (1993) noted that mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research after the publication of John Bowlby's studies.
Original Source
Homeless individuals commonly come from families who are riddled with problems and marital disharmony, and are alienated from their parents. They have often been physically and even sexually abused, have relocated frequently, and many of them may be asked to leave home or are actually thrown out, or alternatively are placed in group homes or in foster care. They often have no one to care for them and no one knows them intimately.
Source from:
Rokach, A. (2005). The causes of loneliness in homeless youth. The Journal of Psychology , 139, 469-480.
Example: Incorrect Paraphrasing
The homeless come from families with problems. Frequently, they have been physically or sexually abused, or have lived in group homes. Usually no one cares for them or knows them intimately (Rokach, 2005).
Note : In this incorrect example the writing is too similar to the original source. The student only changed or removed a few words and has not phrased the ideas in a new way.
Example: Correct Paraphrasing
Many homeless experience isolation in part due to suffering from abuse or neglect during their childhood (Rokach, 2005).
Note : The example keeps the idea of the original writing but phrases it in a new way.
In-Text Citation For Two or More Authors/Editors
| Number of Authors/Editors | First Time Paraphrased | Second and Subsequent Times Paraphrased | First Time Quoting | Second and Subsequent Times Quoting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two | (Case & Daristotle, 2011) | (Case & Daristotle, 2011) | (Case & Daristotle, 2011, p. 57) | (Case & Daristotle, 2011, p. 57) |
| Three or more | (Case et al., 2011) | (Case et al., 2011) | (Case et al., 2011, p. 57) | (Case et al., 2011, p. 57) |
| Type of Group | First Time Paraphrased | Second and Subsequent Times Paraphrased | First Time Quoting | Second and Subsequent Times Quoting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups readily identified through abbreviations | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH, 2003) | (NIMH, 2003) | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH, 2003, p. 5) | (NIMH, 2003, p. 5) |
| Groups with no abbreviations | (University of Pittsburgh, 2005) | (University of Pittsburgh, 2005) | (University of Pittsburgh, 2005, p. 2) | (University of Pittsburgh, 2005, p. 2) |
No Known Author:
Note that in most cases where a personal author is not named, a group author may be cited instead (eg. Statistics Canada). However, in certain cases, such as religious ancient texts, the author is unknown. Where you'd normally put the author's last name, instead use the first one, two, or three words from the title. Don't count initial articles like "A", "An" or "The". You should provide enough words to make it clear which work you're referring to from your References List.
If the title in the References list is in italics, italicize the words from the title in the in-text citation.
If you are citing an article, a chapter of a book or a page from a website, put the words in double quotation marks.
Capitalize the titles using title case (every major word is capitalized) even if the reference list entry uses sentence case (only first word is capitalized).
( Cell Biology , 2012, p. 157)
("Nursing," 2011, p. 9)
No Known Date of Publication :
Where you'd normally put the year of publication, instead use the letters "n.d.".
(Smith, n.d., p. 200)
- << Previous: Quoting
- Next: Works Cited in Another Source >>
- Last Updated: Sep 19, 2024 6:43 PM
- URL: https://columbiacollege-ca.libguides.com/apa

APA 7: Quote & Paraphrase
- Paper Sections
- Quote & Paraphrase
- Format in Word
- In-Text Citations
- Reference List
- Sample Paper
Paraphrase or Summarize
When you paraphrase, you restate the ideas of another writer in your own words. A summary shortens information into a more general statement. For the in-text citation, APA requires the name of the author (or the work's title if the author is unknown) and the year of publication.
- Vonnegut (1982) explains that when writers do not structure and organize their information in meaningful ways, the reader will feel neglected.
- When writers do not structure and organize their information in meaningful ways, the reader will feel neglected (Vonnegut, 1982).
APA encourages including a page range for a summary or paraphrase if it will help the reader find the information in a longer work.
- Paraphrasing - APA Style Guide
Use quotations when you directly quote a source word-for-word in your paper. Use direct quotations when you need an exact definition or when an author has said something memorable or succinctly.
Short Quotations
Short quotations have fewer than 40 words. They require the author, year of publication, and page number (preceded by p.). Place quotation marks around the quote.
- "If you scribble your thoughts any which way, your readers will surely feel that you care nothing about them" (Vonnegut, 1982, p. 150).
Or, with the signal phrase:
- According to Vonnegut (1982), "If you scribble your thoughts any which way, your readers will surely feel that you care nothing about them" (p. 150).
Partial Quotes
If you decide to leave out part of a quotation within your paper, you must still let your reader know that you have left out part of the quote. This is where an ellipsis (...) is needed.
- In "How to Write with Style," famed sci-fi writer Kurt Vonnegut (1982) notes that "I myself find that I trust my writing...when I sound most like a person from Indianapolis" (p. 152).
Long Quotations (Block Quotations)
Quotes longer than 40 words need to be block quotations:
- Do not use quotation marks around the quote.
- Start a block quote on a new line and indent the whole block 0.5 inches from the left margin.
- Double-space the quotation and do not add an extra line before or after it.
- Either cite the source in parentheses after the quotation’s final punctuation or cite the author and year in your paper before the quotation and place only the page number in parentheses after the quotation’s final punctuation.
- Do not add a period after the closing parenthesis.
Researchers have studied how people talk to themselves:
- Quotations - APA Style Guide
- << Previous: Paper Sections
- Next: Format in Word >>

APA Citation Guide (7th edition): Quotes vs Paraphrases
- Book Examples
- Article Examples
- Media Examples
- Internet Resources Examples
- Other Examples
- Quotes vs Paraphrases
- Reference Entry Components
- Paper Formatting
What's the Difference?
Quoting vs paraphrasing: what's the difference.
There are two ways to integrate sources into your assignment: quoting directly or paraphrasing.
Quoting is copying a selection from someone else's work, phrasing it exactly as it was originally written. When quoting place quotation marks (" ") around the selected passage to show where the quote begins and where it ends. Make sure to include an in-text citation.
Paraphrasing is used to show that you understand what the author wrote. You must reword the passage, expressing the ideas in your own words, and not just change a few words here and there. Make sure to also include an in-text citation.
Quoting Example
There are two basic formats that can be used:
Parenthetical Style:
Narrative Style:
Quoting Tips
- Long Quotes
- Changing Quotes
What Is a Long Quotation?
A quotation of more than 40 words.
Rules for Long Quotations
There are 4 rules that apply to long quotations that are different from regular quotations:
- The line before your long quotation, when you're introducing the quote, usually ends with a colon.
- The long quotation is indented half an inch from the rest of the text, so it looks like a block of text.
- There are no quotation marks around the quotation.
- The period at the end of the quotation comes before your in-text citation as opposed to after, as it does with regular quotations.
Example of a Long Quotation
At the end of Lord of the Flies the boys are struck with the realization of their behaviour:
The tears began to flow and sobs shook him. He gave himself up to them now for the first time on the island; great, shuddering spasms of grief that seemed to wrench his whole body. His voice rose under the black smoke before the burning wreckage of the island; and infected by that emotion, the other little boys began to shake and sob too. (Golding, 1960, p.186)
Changing Quotations
Sometimes you may want to make some modifications to the quote to fit your writing. Here are some APA rules when changing quotes:
Incorrect spelling, grammar, and punctuation
Add the word [sic] after the error in the quotation to let your reader know the error was in the original source and is not your error.
Omitting parts of a quotation
If you would like to exclude some words from a quotation, replace the words you are not including with an ellipsis - ...
Adding words to a quote
If you are adding words that are not part of the original quote, enclose the additional words in square brackets - [XYZ]
Secondary Source Quotes
What is a secondary source.
In scholarly work, a primary source reports original content; a secondary source refers to content first reported in another source.
- Cite secondary sources sparingly—for instance, when the original work is out of print, unavailable, or available only in a language that you do not understand.
- If possible, as a matter of good scholarly practice, find the primary source, read it, and cite it directly rather than citing a secondary source.
Rules for Secondary Source Citations
- In the reference list, provide an entry only for the secondary source that you used.
- In the text, identify the primary source and write “as cited in” the secondary source that you used.
- If the year of publication of the primary source is known, also include it in the in-text citation.
Example of a Secondary Source Use
Quote & In-Text Citation
Reference List Entry
Paraphrases
Paraphrasing example.
When you write information from a source in your own words, cite the source by adding an in-text citation at the end of the paraphrased portion as follows:
If you refer to the author's name in a sentence you do not have to include the name again as part of your in-text citation, instead include the year of publication following his/her name:
NOTE : Although not required, APA encourages including the page number when paraphrasing if it will help the reader locate the information in a long text and distinguish between the information that is coming from you and the source.
Paraphrasing Tips
- Long Paraphrases
Original Source
Homeless individuals commonly come from families who are riddled with problems and marital disharmony, and are alienated from their parents. They have often been physically and even sexually abused, have relocated frequently, and many of them may be asked to leave home or are actually thrown out, or alternatively are placed in group homes or in foster care. They often have no one to care for them and no one knows them intimately.
Source from:
Rokach, A. (2005). The causes of loneliness in homeless youth. The Journal of Psychology, 139, 469-480.
Example: Incorrect Paraphrasing
Example: correct paraphrasing.
If your paraphrase is longer than one sentence, provide an in-text citation for the source at the beginning of the paraphrase. As long as it's clear that the paraphrase continues to the following sentences, you don't have to include in-text citations for the following sentences.
If your paraphrase continues to another paragraph and/or you include paraphrases from other sources within the paragraph, repeat the in-text citations for each.
Additional Resource
- Paraphrasing (The Learning Portal)
Tip sheet on paraphrasing information
- << Previous: In-Text Citations
- Next: Reference Entry Components >>
- Last Updated: Jul 30, 2024 4:42 PM
- URL: https://simmons.libguides.com/apa
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
In-Text Citations: The Basics

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here .
Reference citations in text are covered on pages 261-268 of the Publication Manual. What follows are some general guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay.
Note: On pages 117-118, the Publication Manual suggests that authors of research papers should use the past tense or present perfect tense for signal phrases that occur in the literature review and procedure descriptions (for example, Jones (1998) found or Jones (1998) has found ...). Contexts other than traditionally-structured research writing may permit the simple present tense (for example, Jones (1998) finds ).
APA Citation Basics
When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
If you are referring to an idea from another work but NOT directly quoting the material, or making reference to an entire book, article or other work, you only have to make reference to the author and year of publication and not the page number in your in-text reference.
On the other hand, if you are directly quoting or borrowing from another work, you should include the page number at the end of the parenthetical citation. Use the abbreviation “p.” (for one page) or “pp.” (for multiple pages) before listing the page number(s). Use an en dash for page ranges. For example, you might write (Jones, 1998, p. 199) or (Jones, 1998, pp. 199–201). This information is reiterated below.
Regardless of how they are referenced, all sources that are cited in the text must appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
In-text citation capitalization, quotes, and italics/underlining
- Always capitalize proper nouns, including author names and initials: D. Jones.
- If you refer to the title of a source within your paper, capitalize all words that are four letters long or greater within the title of a source: Permanence and Change . Exceptions apply to short words that are verbs, nouns, pronouns, adjectives, and adverbs: Writing New Media , There Is Nothing Left to Lose .
( Note: in your References list, only the first word of a title will be capitalized: Writing new media .)
- When capitalizing titles, capitalize both words in a hyphenated compound word: Natural-Born Cyborgs .
- Capitalize the first word after a dash or colon: "Defining Film Rhetoric: The Case of Hitchcock's Vertigo ."
- If the title of the work is italicized in your reference list, italicize it and use title case capitalization in the text: The Closing of the American Mind ; The Wizard of Oz ; Friends .
- If the title of the work is not italicized in your reference list, use double quotation marks and title case capitalization (even though the reference list uses sentence case): "Multimedia Narration: Constructing Possible Worlds;" "The One Where Chandler Can't Cry."
Short quotations
If you are directly quoting from a work, you will need to include the author, year of publication, and page number for the reference (preceded by "p." for a single page and “pp.” for a span of multiple pages, with the page numbers separated by an en dash).
You can introduce the quotation with a signal phrase that includes the author's last name followed by the date of publication in parentheses.
If you do not include the author’s name in the text of the sentence, place the author's last name, the year of publication, and the page number in parentheses after the quotation.
Long quotations
Place direct quotations that are 40 words or longer in a free-standing block of typewritten lines and omit quotation marks. Start the quotation on a new line, indented 1/2 inch from the left margin, i.e., in the same place you would begin a new paragraph. Type the entire quotation on the new margin, and indent the first line of any subsequent paragraph within the quotation 1/2 inch from the new margin. Maintain double-spacing throughout, but do not add an extra blank line before or after it. The parenthetical citation should come after the closing punctuation mark.
Because block quotation formatting is difficult for us to replicate in the OWL's content management system, we have simply provided a screenshot of a generic example below.

Formatting example for block quotations in APA 7 style.
Quotations from sources without pages
Direct quotations from sources that do not contain pages should not reference a page number. Instead, you may reference another logical identifying element: a paragraph, a chapter number, a section number, a table number, or something else. Older works (like religious texts) can also incorporate special location identifiers like verse numbers. In short: pick a substitute for page numbers that makes sense for your source.
Summary or paraphrase
If you are paraphrasing an idea from another work, you only have to make reference to the author and year of publication in your in-text reference and may omit the page numbers. APA guidelines, however, do encourage including a page range for a summary or paraphrase when it will help the reader find the information in a longer work.

APA 7th Edition Citation Guide
- General APA Style Guidelines
- Book and eBook Examples
- Article Examples
- Multimedia Examples
- Visual Works Examples
- Social Media Examples
- Personal Communication and Interview Examples
- Artificial Intelligence
- In-Text (Parenthetical) Examples
- Annotated Bibliography
- Other Citation Styles
Good to know
The punctuation at the end of the sentence goes after and outside the parenthesis.
I am paraphrasing (Smith, 2019).
If you are using a direct quote, there is no comma between the end of the quotation and the in-text citation.
"this is a quote" (Smith, 2019, p. 263).
|
If paraphrasing, in parenthesis, list the author's last name followed by a comma and the year of publication. The punctuation at the end of the sentence goes after and outside the parenthesis. (Author's last name, year) |
Citing sources is very important (Smith, 2019). |
|
If directly quoting, in parenthesis, list the author's last name followed by a comma and the year of publication followed by a comma and the page number(s).
(Author's last name, year, page number) |
It should be noted that "proper usage of citations is crucial" (Smith, 2019, p. 263) |
| If you are citing multiple pages use pp. (Smith, 2019, pp. 17-27) | |
|
If paraphrasing the author in text, list the author in the sentence without parenthesis, include the year of publication in parenthesis immediately afterwards and then the paraphrased information. List the Author's last name (year) and the paraphrased information in your sentence. |
Smith (2019) states citing sources is very important. |
|
If directly quoting the author in text, list the author in the sentence without parenthesis, include the year of publication in parenthesis immediately afterwards and then the quoted information. List page number(s) at the end of the sentence in parenthesis.
List the Author's last name (year), "direct quotation inside quotation marks" (p. #). |
In his article on citations, Smith (2019) states that "proper usage of citations is crucial" (p. 263). |
|
If there is no author, list a shortened version of the title in place of the author followed by a comma and the year of publication. For example: If the article is entitled "Very long work can be exhausting to read," the title can be shortened to "Very long work."
("shortened title", year) |
This article is very long ("Very long work," 2019). |
| If directly quoting, after the year of publication add a comma and put the page number | |
|
If paraphrasing two authors, list the last names of both authors connected with "&" followed by a comma and the year of publication.
(Author's last name & Second author's last name, year) |
Citations are academically honest (Smith & Jones, 2019). |
| If directly quoting, after the year of publication add a comma and put the page number | |
|
If paraphrasing three or more authors, list the first author followed by “et al.” followed by a comma and the year of publication. (Author's last name et al. year) |
Citations have saved millions of papers (Smith et al., 2019). |
| If directly quoting, after the year of publication add a comma and put the page number | |
|
If using a group or corporate author, list the name or abbreviation of the group/company/agency in place of the author; followed by a comma and the year of publication.
(Group name, year) |
It has been reported that failure to use citations is a threat to national security (Citation Security Agency, 2019). |
| If directly quoting, after the year of publication add a comma and put the page number | |
|
If you are using text generated by an AI, please use the company's name who owns the product and the year you used it. (AI Company, year) |
The citation was long and written by ChatGPT ( , ). |
| Always directly quote when AI is used, unless otherwise stated by your professor. | |
|
If there is no date, put (n.d.) for year. Place a period after n and d with no spaces in between. (Author last name, year) |
The citation was long but did not have a date (Smith, n.d.) |
| If directly quoting, after the year of publication add a comma and put the page number The "n.d." stands for "No Date." Be sure to use n.d. on the References page to match the in-text citation. | |
|
If there are two or more authors with the same last name, list the first name initial(s) and then the last name followed by a comma and then the year.
(First author first initial. last name, year). (Second author first initial. last name, year).
|
The glass is half full (A. Smith, 2019). The glass is half empty (B. Smith, 2019). |
| If directly quoting, after the year of publication add a comma and put the page number | |
|
If multiple references have an identical author (or authors) and year of publication, list a lowercase letter after the year. The References page for these citations needs to have the year of publication exactly match the in-text date with the added lowercase letter. (Author last name, yeara). (Author last name, yearb)
|
(Redd, 2017a). (Redd, 2017b).
|
| If directly quoting, after the year of publication add a comma and put the page number | |
|
If you are citing a work in translation, you write the year of initial publication followed by the year of the translation's publication, separated by a forward slash. (Author last name, Year of Initial Publication/Year of Translation Publication).
|
(Redd, 2017/2019).
|
| If directly quoting, after the year of publication add a comma and put the page number | |
|
If referencing a source that has no page numbers; list the paragraph number, section title, table number, slide number, etc.
Some other sources use the full word, such as Table, Graph, Chart.
|
There is some evidence to suggest that "citations have the potential to help grades" (Smith, 2019, para. 5).
|
| If directly quoting, after the year of publication add a comma and put the page number | |
- << Previous: Artificial Intelligence
- Next: Annotated Bibliography >>
- Last Updated: Sep 19, 2024 8:58 AM
- URL: https://cccs.libguides.com/accapa

Tips on Paraphrasing
- Have you simply changed a few words to synonyms? Try again. Being handy with a thesaurus is not enough to make the sentence yours.
- Have you included exact sequences of words from the original? If so, make sure to put quotation marks around those phrases, or re-write until the entire paraphrase is your words.
- Have you retained the meaning of the original? Changing the author's meaning is not plagiarism, but academic honesty requires you to represent other's work accurately in your writing.
Polivy, J., & Herman, C. P. (2004). Sociocultural idealization of thin female body shapes: An introduction to the special issue on body image and eating disorders. Journal of Social & Clinical Psychology , 23, 1-6. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.134.3.460


A direct quotation reproduces words verbatim from another work or from your own previously published work. It is best to paraphrase sources rather than directly quoting them because paraphrasing allows you to fit material to the context of your paper and writing style.
Use direct quotations rather than paraphrasing:
- when reproducing an exact definition (see Section 6.22 of the Publication Manual ),
- when an author has said something memorably or succinctly, or
- when you want to respond to exact wording (e.g., something someone said).
Instructors, programs, editors, and publishers may establish limits on the use of direct quotations. Consult your instructor or editor if you are concerned that you may have too much quoted material in your paper.
This page addresses how to format short quotations and block quotations. Additional information is available about how to:
- include page numbers for quotations
- cite quotations from material without page numbers
- cite quotations that include errors
- indicate changes to quotations
- present quotations from research participants
Quotations are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Sections 8.25 to 8.35 and the Concise Guide Sections 8.25 to 8.34
Related handout
- In-Text Citation Checklist (PDF, 227KB)
Short quotations (fewer than 40 words)
For quotations of fewer than 40 words, add quotation marks around the words and incorporate the quote into your own text—there is no additional formatting needed. Do not insert an ellipsis at the beginning and/or end of a quotation unless the original source includes an ellipsis.
Effective teams can be difficult to describe because “high performance along one domain does not translate to high performance along another” (Ervin et al., 2018, p. 470).
For a direct quotation, always include a full citation ( parenthetical or narrative ) in the same sentence as the quotation, including the page number (or other location information, e.g., paragraph number).
- Place a parenthetical citation either immediately after the quotation or at the end of the sentence.
- For a narrative citation, include the author and year in the sentence and then place the page number or other location information in parentheses after the quotation.
- If the quotation precedes the narrative citation, put the page number or location information after the year and a comma.
- If the citation appears at the end of a sentence, put the end punctuation after the closing parenthesis for the citation.
- If the quotation includes citations, see Section 8.32 of the Publication Manual .
- If the quotation includes material already in quotation marks, see Section 8.33 of the Publication Manual .
- Place periods and commas within closing single or double quotation marks. Place other punctuation marks inside quotation marks only when they are part of the quoted material.
Block quotations (40 words or more)
Format quotations of 40 words or more as block quotations:
- Do not use quotation marks to enclose a block quotation.
- Start a block quotation on a new line and indent the whole block 0.5 in. from the left margin.
- Double-space the entire block quotation.
- Do not add extra space before or after it.
- If there are additional paragraphs within the quotation, indent the first line of each subsequent paragraph an additional 0.5 in. See an example in Section 8.27 of the Publication Manual .
- Either (a) cite the source in parentheses after the quotation’s final punctuation or (b) cite the author and year in the narrative before the quotation and place only the page number in parentheses after the quotation’s final punctuation.
- Do not add a period after the closing parenthesis in either case.
Block quotation with parenthetical citation:
Researchers have studied how people talk to themselves:
Inner speech is a paradoxical phenomenon. It is an experience that is central to many people’s everyday lives, and yet it presents considerable challenges to any effort to study it scientifically. Nevertheless, a wide range of methodologies and approaches have combined to shed light on the subjective experience of inner speech and its cognitive and neural underpinnings. (Alderson-Day & Fernyhough, 2015, p. 957)
Block quotation with narrative citation:
Flores et al. (2018) described how they addressed potential researcher bias when working with an intersectional community of transgender people of color:
Everyone on the research team belonged to a stigmatized group but also held privileged identities. Throughout the research process, we attended to the ways in which our privileged and oppressed identities may have influenced the research process, findings, and presentation of results. (p. 311)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn how to paraphrase sources in your own words and cite them using APA style. Find examples of long and short paraphrases, citation formats, and tips for avoiding plagiarism.
Learn how to paraphrase in APA style, including steps, examples, and rules for in-text citations. Paraphrasing is the art of putting information into your own words while giving credit to the original source.
Paraphrasing Guidelines (APA, 2020, p. 269) APA 7 notes that "published authors paraphrase their sources most of the time, rather than directly quoting" (p. 269). For writing in psychology, students should use direct quotations only sparingly and instead mainly synthesize and paraphrase. Webster-Stratton (2016) described a case example of a ...
Learn how to paraphrase a quote from a source by restating its essential information and ideas in a new form. Follow the six steps to effective paraphrasing and avoid plagiarism, and see examples of paraphrases and summaries.
Learn how to paraphrase correctly and avoid plagiarism by changing the wording of a source while preserving the meaning. See examples of paraphrasing different types of sources and compare it with quoting and summarizing.
Practice your paraphrasing and citation skills with three activities that involve summarizing sentences, paragraphs, and studies from published works. Compare your answers with the APA Style team and learn how to avoid patchwriting and emphasize different ideas.
Note: In this incorrect example the writing is too similar to the original source. The student only changed or removed a few words and has not phrased the ideas in a new way. Example: Correct Paraphrasing. Many homeless experience isolation in part due to suffering from abuse or neglect during their childhood (Rokach, 2005).
When paraphrasing or summarising using one source over several sentences or even a whole paragraph, cite the source in the first sentence. There is no need to cite the work again in this paragraph provided it is clear that this is the only source being paraphrased. The APA Style and Grammar Guidelines provide this example: Velez et al. (2018 ...
Learn how to paraphrase and quote sources in APA Style, including when and how to include page numbers or other location information. Find examples, advice, and answers to common questions about paraphrasing and quoting.
The APA requires a paraphrase to include the author's last name and the work's year of publication, but also suggests that the page number of the original text be included. ... Note: This example includes the in-text citations of three works arranged in alphabetical order by authors' names, separated by semi-colons, and enclosed in ...
How to Paraphrase in APA Examples. ... Paraphrasing in APA is an essential skill for any student or researcher. By understanding the intricacies of APA citation style, distinguishing between citations and paraphrases, and following our tips for correct paraphrasing, you can ensure your academic work is both credible and free from plagiarism. ...
Let's look at these examples if they were written in text: An example with 1 author: Parenthetical citation: Following American Psychological Association (APA) style guidelines will help you to cultivate your own unique academic voice as an expert in your field (Forbes, 2020). Narrative citation: Forbes (2020) shared that by following American Psychological Association (APA) guidelines ...
General Guidelines for Paraphrasing and Summarizing. Paraphrasing is when you put a passage or idea from another work into your own words. A paraphrased passage is generally shorter and more condensed than the original. You can cite your information as part of the sentence (called a narrative citation) or at the end in parentheses (known as a ...
The student only changed or removed a few words and has not phrased the ideas in a new way. Example: Correct Paraphrasing. Many homeless experience isolation in part due to suffering from abuse or neglect during their childhood (Rokach, 2005). Note: The example keeps the idea of the original writing but phrases it in a new way.
Paraphrase and Summary: Incorporate a portion of the source into your essay by conveying its meaning in your own words. Paraphrase aims to replicate all of the ideas of the source passage, while summary aims to express only its main point(s).; Are introduced by a signal phrase, incorporating the source passage into the flow of the essay.
Paraphrasing. When you write information from a source in your own words, cite the source by adding an in-text citation at the end of the paraphrased portion as follows: Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt, 1993). Note: If you refer to the author's ...
Start a block quote on a new line and indent the whole block 0.5 inches from the left margin. Double-space the quotation and do not add an extra line before or after it. Either cite the source in parentheses after the quotation's final punctuation or cite the author and year in your paper before the quotation and place only the page number in ...
Paraphrasing Example. When you write information from a source in your own words, cite the source by adding an in-text citation at the end of the paraphrased portion as follows: ... APA encourages including the page number when paraphrasing if it will help the reader locate the information in a long text and distinguish between the information ...
Learn how to acknowledge the work of others in your scholarly writing with APA Style in-text citations. Find out how to format interviews, classroom and intranet sources, personal communications, paraphrases and direct quotations, and more.
Learn how to cite sources in APA style using the author-date method, with examples of quotations, paraphrases, and block quotations. Find out how to format titles, capitalization, and page numbers in your in-text citations.
Basic format (Paraphrasing) Components. If paraphrasing, in parenthesis, list the author's last name followed by a comma and the year of publication. The punctuation at the end of the sentence goes after and outside the parenthesis. (Author's last name, year) Example. Citing sources is very important (Smith, 2019).
Paraphrase in Paper (APA) If a woman interprets the media's representation of thinness as the ideal she must achieve, her sense of self-esteem might be threatened and even damaged, making her more likely to exhibit disordered eating patterns (Polivy & Herman, 2004, p. 2). Note: APA does not require a page number reference for summaries, but you ...
Learn how to format short and long quotations in APA style, with examples and rules for punctuation, citation, and quotation marks. Find out how to handle quotations from sources without page numbers, with errors, or from research participants.